This posting is part of Coupang Partners activity, and I receive a certain amount of commission accordingly.
Kale is known as a superfood packed with various nutrients and antioxidants. It is rich in several types of antioxidants, including vitamin C, beta-carotene, kaempferol, and quercetin. In this article, we will take a closer look at the health benefits of kale.
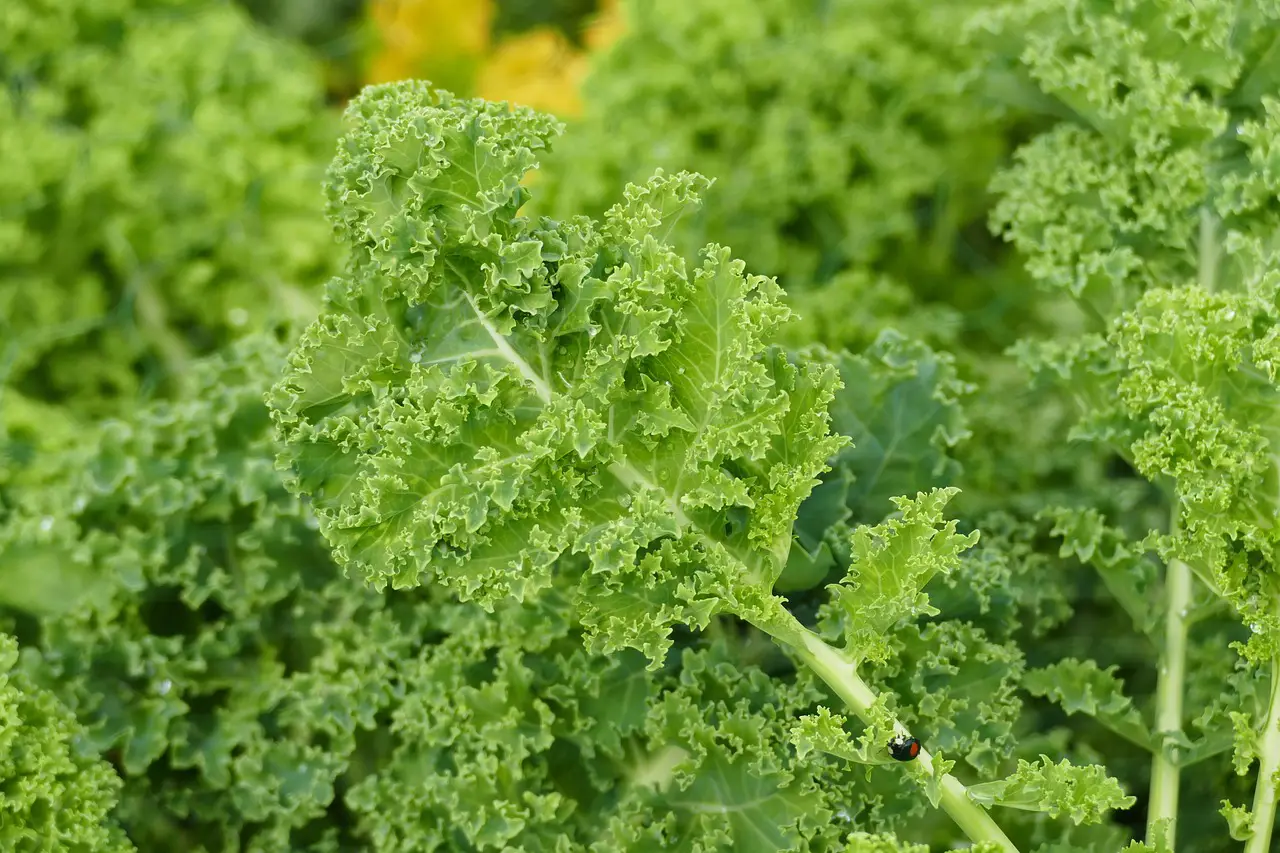

Kale Nutritional Information
Here are the main nutrients contained in 100g of raw kale:
- Vitamin A (Beta-Carotene): 241mcg
- Vitamin C: 93.4mg
- Vitamin B2: 0.35g
- Folate: 62mcg
- Vitamin K: 389.6mcg
- Calcium: 254mg
- Iron: 348mg
- Magnesium: 33mg
- Manganese: 0.92mg
Kale Benefits
Rich in Antioxidants
This vegetable contains more than 45 types of flavonoids, including kaempferol and quercetin. Flavonoids provide strong antioxidant effects that support our health.
Excellent Source of Vitamin K
Vitamin K is an essential nutrient for health, helping to lower blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health. It also offers various health benefits, such as increasing bone density and preventing blood clotting.
Effective for Detox and Weight Loss
This vegetable is rich in dietary fiber and sulfur, with 5g of fiber per cup. Regular consumption can improve digestive function, support liver health, and provide detox benefits.
A serving of about one cup contains only 36 kcal and 0g of fat. Despite being low in calories, it contains important proteins and dietary fiber that are beneficial for weight loss. It is also rich in vitamins, folate, and magnesium, which help promote a feeling of fullness, making it effective for dieting.
Moreover, this vegetable provides 134% of the daily recommended intake of vitamin C, which helps with hydration and metabolism, improving blood sugar levels and supporting weight loss.
Effective in Preventing Various Diseases
Like other green vegetables, kale helps prevent several types of cancer, including colorectal, prostate, and ovarian cancer. The vitamin K in kale strengthens bones and helps prevent osteoporosis, while folate and vitamin B6 improve cardiovascular health and contribute to the prevention of heart disease.
Helps Boost Immunity
The rich nutrients in kale strengthen the immune system and are effective in reducing the number of viruses and bacteria. This vegetable contains more iron than beef, making it an excellent source of this essential mineral for vegans and vegetarians. These minerals help oxygenate the bloodstream, making it especially beneficial for those with anemia.
Helps Improve Vision
Kale is known to be rich in vitamin A, but in reality, it contains a large amount of beta-carotene, not vitamin A. Beta-carotene is an antioxidant that is converted into vitamin A in the body. Therefore, regular consumption can help increase vitamin A levels in the body.
This vegetable contains lutein, zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene as its main components. According to research, consistently consuming lutein and zeaxanthin is effective in reducing the risk of cataracts and vision deterioration.
Helps with Infant Brain Development
This vegetable is rich in folate, which plays an important role in fetal brain development. Therefore, regular consumption can help prevent congenital defects, promote normal weight and healthy neural tube development, and have a positive impact on the formation of the face and heart.
Cooking Recipe and How to Eat
Kale Chips
Kale chips are a low-calorie snack that is packed with nutrients. The preparation is simple and quick.
Ingredients: 1 bunch of kale, 1 tablespoon of olive oil, 1 teaspoon of seasoned salt
Cooking time: 20 minutes
- Preheat the oven to 350°F (175°C) and line a baking sheet with parchment paper.
- Use a knife or kitchen scissors to remove the kale leaves from the stems and cut them into bite-sized pieces.
- Wash the cut kale leaves thoroughly with water and dry them well to remove excess moisture.
- Toss the dried kale leaves with olive oil and seasoned salt, ensuring they are evenly coated.
- Bake in the oven for about 10-15 minutes, until the edges of the leaves turn brown.
Be careful not to burn them while baking.
Side Effects and Precautions
If you have kidney disease, you should avoid excessive potassium intake. If the kidneys cannot properly excrete excess potassium, it can have serious health consequences.
Kale is a vegetable rich in vitamin K, which can cause issues related to blood clotting. If you have blood clotting problems, it is recommended to avoid consuming kale.
This information is for general reference and is not medical advice. If you have health issues, are taking medication, or have special circumstances, it is important to consult a healthcare professional first.


Leave a Comment